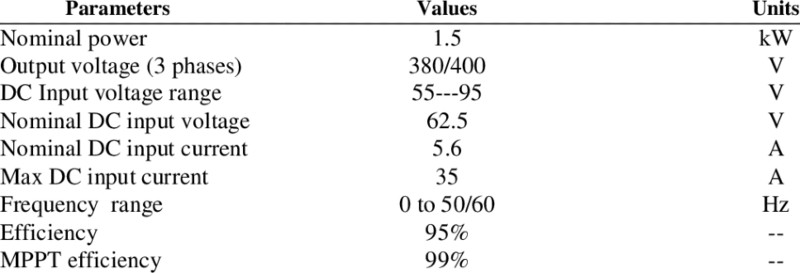
When you’re getting your solar power system up and running, safety should be at the top of your list.
And a big part of that is grounding. But what is negative grounding in a solar inverter exactly?
It’s pretty straightforward: you connect the negative terminal of your solar panels to the ground.
This setup ensures that if there’s any unexpected surge of electricity (like in a fault), it has a safe route to travel, which keeps everything safe and running smoothly.
In this article, I’ll walk you through how negative grounding works, why it’s important, and the benefits it brings to your solar power system.
Key Takeaways
- Negative grounding in a solar inverter connects the negative terminal of your solar panels to the ground using a conductive wire and grounding electrode.
- It provides a safe path for fault currents, allowing circuit breakers and fuses to cut off power in case of electrical faults.
- Negative grounding reduces electrical noise and interference, improving power quality and making the inverter operate more efficiently.
- It helps prevent galvanic corrosion by stabilizing the electrical environment and extending the lifespan of solar components.
- Following electrical codes and safety standards ensures negative grounding is implemented correctly, enhancing system safety and reliability.
What Is Grounding in Electricity?
Grounding, or earthing, is what gives an electrical circuit a safe way to get rid of extra voltage, making the whole system safer.
In a typical household electrical setup, “ground” means “earth ground.”
This usually involves a metal rod driven into the soil or another connection to the earth outside your home.
This setup provides a path for any excess electricity to flow into the ground safely.
Related article: How To Read Solar Inverter Specifications?
How Does Negative Grounding Work in a Solar Inverter?
Negative grounding in a solar inverter works by creating a connection between the negative terminal of your solar panels and the ground.
This is done using a grounding conductor, which is the name for a wire that’s made from materials that are good at conducting electricity—like copper or aluminum.
To make sure this wire lasts a long time and doesn’t get damaged by moisture or other environmental factors, it’s insulated.
Now, at the heart of this setup is something called a grounding electrode.
This could be a metal rod, a plate, or some other conductive item that gets buried in the ground.
It’s super important because it’s where the connection to the earth is made.
Linking the solar system to the earth through this electrode helps to keep the electrical potential—the energy levels—between your system and the ground stable.
This is crucial because it prevents electrical problems that could harm your system.
This grounding arrangement also paves a clear path for something called fault currents.
These are unexpected surges of electricity that can happen if there’s a short circuit or some other issue.
It’s important to have a designated route for these surges to safely return to the ground; otherwise, they could cause damage.
Once this path is all setup, it lets protective gear like circuit breakers, fuses, and ground fault protection relays do their job properly.
These devices keep an eye on the electricity flowing through your system and quickly react if they spot anything out of the ordinary.
They shut down the power to the problem area, preventing any further damage and keeping your solar power system safe.
And remember, following electrical codes and safety standards is important to make sure everything works together safely and effectively.
In the US, we have the National Electrical Code (NEC), and in India, there are the Indian Electrical Rules.
These standards give us the guidelines we need to ground solar projects correctly, boosting both safety and reliability.
Related article: Can You Connect An Inverter Directly To A Solar Panel?
What Are the Benefits of Negative Grounding in a Solar Inverter?
1. Enhancing Safety Measures
As I mentioned before, a negative grounding in your solar inverters gives you two big benefits: it cuts down on electric shock risks and guards against electrical faults.
So here’s the deal: by connecting the negative terminal to the ground, we create what’s called a low-resistance path straight to the earth.
This setup is super important because it greatly lowers the chance of anyone getting shocked while they’re working on or around the solar system.
It quickly gets rid of any fault currents or weird voltage imbalances by sending them into the ground before they can cause any trouble.
This is a key move in stopping voltage from building up between the different parts of your solar system, which is often what leads to electric shocks.
Then, if something goes wrong, like a fault or short circuit, negative grounding shows its worth by making sure those stray currents get safely carried away to the earth.
This is a big deal because it means both the people and the equipment are protected from any harm.
By effectively managing these unexpected jolts of electricity, negative grounding keeps the whole solar system safe and sound.
2. Identifying and Mitigating Faults
Negative grounding doesn’t just protect; it also plays a crucial role in quickly spotting and handling ground faults.
What’s a ground fault?
It happens when there’s an unintended connection between the conductive elements of your PV system and the earth.
These are not just minor glitches; they can lead to serious issues if not addressed promptly.
With negative grounding, these faults are easier to detect and fix.
Because the system is grounded to the earth, any stray electricity that isn’t supposed to be there gets noticed much faster.
This quick detection is key because it allows you to address the issue before it can cause damage or lead to safety hazards.
3. Boosting System Performance
Performance and efficiency are huge perks of using negative grounding in your solar inverter system.
Here’s the scoop: negative grounding stabilizes the electrical environment around your inverter.
This means it cuts down a ton of electrical noise and interference.
Why does this matter?
Well, it helps your inverter run smoothly without getting tripped up by weird electrical signals.
Less interference means better power quality, and that lets your system convert sunlight to electricity more efficiently and effectively.
But there’s more to it.
Negative grounding also makes your system smarter at spotting and fixing problems quickly.
With solid grounding, if anything odd pops up—like unexpected electrical connections—your system notices it right away.
This quick detection is a game changer because it lets you jump right into troubleshooting and fixing issues before they get out of hand.
4. Improving Protective Device Effectiveness
Protective devices like fuses and circuit breakers are the unsung heroes of your solar power system, and having negative grounding gives them a big boost.
Here’s the thing: negative grounding creates a straight, clear path for any faulty currents to safely zing back to the ground.
This allows these protective devices to work at their best.
Let’s say there’s a hiccup in your system—maybe an overload or a short circuit.
Circuit breakers are always on guard for these kinds of issues.
When they detect something off, they react super fast, kind of like hitting an emergency stop button, and cut off the power right away.
This swift action is key because it stops too much current from flowing through the system, which can prevent a bunch of problems, like overheating or even fires.
Fuses have a similar job.
They’re designed to fail safely—yes, on purpose!
They “blow up” (safely, inside their casing) when the current gets too high.
This breaks the connection and stops the electricity flow dead in its tracks, protecting your system from further damage.
With a negative grounding in place, these devices can respond even quicker, significantly boosting the safety of your entire solar system.
The clear path it provides for fault currents means that circuit breakers and fuses can effectively handle electrical faults, boosting their protective capabilities.
5. Avoiding Corrosion Risks
Corrosion risks, such as galvanic corrosion, can be a problem for solar power systems, especially if they’re located in damp environments.
Let’s unpack this a bit: galvanic corrosion occurs when different metals in your system are exposed to moisture.
This can make part of your solar setup act like a battery, where one metal starts to degrade another due to electrical currents flowing between them.
This isn’t ideal because it can significantly reduce the lifespan of your system’s components.
That’s where the magic of grounding the negative terminal comes into play.
By connecting it to the ground, you help stabilize the electrical environment around these metals.
Why does this matter?
Well, it prevents the formation of those troublesome galvanic cells.
It does this by balancing out the electrical potential between the different metals in the system, which stops the unwanted flow of electrons that causes corrosion.
In simpler terms, grounding the negative terminal gives your system a way to handle and neutralize those pesky electrical imbalances that can lead to corrosion.
This is not just about maintaining stability; it’s a critical measure that acts as a protective barrier.
Related article: Can A Solar Panel Work Without An Inverter?
Can I Upgrade Existing Solar Power Systems with Negative Grounding?
You can upgrade your existing solar power system with negative grounding, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution.
Whether you can add it depends on the particular components and layout of your system.
Here’s the best way to go about it: before you start making any changes, it’s important to talk to a solar professional or a licensed electrician.
They can examine your setup in detail and tell you if you can safely and effectively implement negative grounding.
If you do go ahead with retrofitting negative grounding, you might need to make some adjustments.
These could include changing the wiring, tweaking the grounding electrodes, or adjusting the settings on your inverter.
In these cases, I recommend you get an expert to take a look.
They’ll check everything to ensure that the changes you make are safe and won’t interfere with how well your system works.
Related article: How To Protect Your Solar Inverter From Lightning?
How Can You Determine If Your Solar Inverter Has Negative or Positive Grounding?
You can determine if your solar inverter uses negative or positive grounding with a few straightforward steps.
First off, grab the user manual or product specification sheet that came with your inverter.
These documents are handy because they usually detail how the system is grounded and can tell you if it’s set up with negative or positive grounding.
If you don’t have access to these documents or if the information isn’t clear, no worries—you can check the inverter yourself.
Just take a look at where the grounding conductor is connected.
If it’s attached to the negative terminal of your photovoltaic (PV) array, then your system is using negative grounding.
On the other hand, if it’s connected to the positive terminal, then your system has positive grounding.
Not so sure about checking the system on your own or still a bit confused?
A multimeter can be your best friend here.
Use it to check for continuity between the grounding conductor and the terminals.
Whichever terminal—be it negative or positive—shows continuity with the grounding conductor is the one that’s grounded.
Still, feeling uncertain?
It might be time to call in an expert.
A qualified solar professional or licensed electrician can perform a thorough inspection and accurately determine the grounding type of your inverter.
Plus, many modern inverters come with built-in indicators or software interfaces that display the grounding type right on the unit, which makes things even easier.
FAQs
Does a Solar Inverter Need to Be Grounded?
A solar inverter needs to be grounded for safety and system stability, reducing the risk of electrical faults and shocks.
What Does Negative Grounding Mean?
Negative grounding means connecting the negative terminal of a solar system to the ground, helping manage electrical imbalances and prevent corrosion.
What Is Negative Grounding PV Array Configuration?
A negative grounding PV array configuration is where the negative terminal of the PV array is connected to the ground to enhance safety and system performance.
What Is the Difference Between Positive Ground and Negative Ground Solar Panels?
The difference between positive ground and negative ground solar panels is that positive ground connects the positive terminal to the ground, while negative ground connects the negative terminal, each affecting current flow direction and potential corrosion risks.
Conclusion
As promised, we’ve covered the basics of negative grounding in solar inverters—what it is, why it’s important, and how to set it up.
Negative grounding boosts safety, makes your system run better, and stops problems like galvanic corrosion.
And here’s a pro tip: regularly check your grounding connections, especially after bad weather, to keep them working well.
I always recommend setting a reminder to do a quick check every few months.
This small habit can save you from bigger headaches down the road and ensure your solar setup continues to run smoothly and efficiently for years to come.